Top 5 Career Options After a Diploma in Tool Engineering
November 15, 2025 2025-11-18 9:35Top 5 Career Options After a Diploma in Tool Engineering

The Diploma in Tool Engineering is more than just an educational qualification – it is a steppingstone to the most important sectors of the world. From the car you drive home to the medical equipment in the hospital or even the phone in your pocket, none of these inventions could have been made without the accuracy of the tools, dies and moulds developed by trained professionals.
The design of tools is a science and art that involves technical expertise and creativity in solving problems. Having this qualification will lead you towards a successful and future-proof career in manufacturing, designing, and product innovation.
Why Do Tool Engineers Matter?
Mass production requires that industries have tools, dies, and moulds that have been engineered to perfection in order to reproduce products with unblemished accuracy.
That’s the reason tool engineers, tool makers, and CNC programmers are of great importance here. Millions of everyday items from bottle tops and gears to syringes and smartphone cases are made one at a time through advanced tooling processes. The automotive industry, aerospace industry, consumer electronics industry, and medical devices industry would grind to a halt in the absence of them.
Thinking in 3D, thinking of innovations, and creating specific tools are qualities peculiar to people even in times of AI and automation. This is why tool design is a highly demanding career option for the future.
Top 5 Career Pathways After a Diploma in Tool Engineer
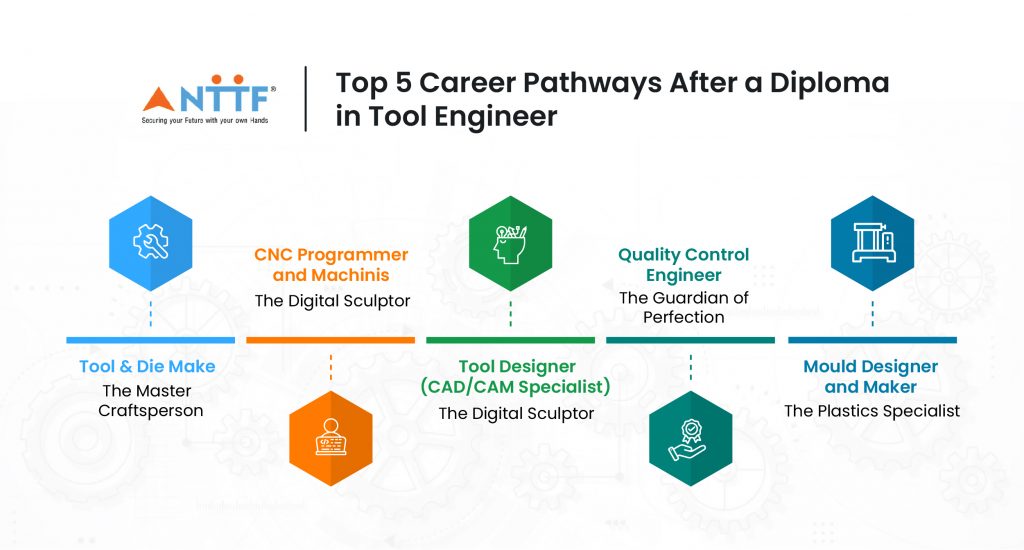
1. Tool & Die Maker – The Master Craftsperson
- Role: Turn engineering drawings into practical reality using milling, CNC machines, lathes, and grinders.
- Key Skills: Die assembly, precision machining, and tool maintenance.
- Why It Matters: The backbone of manufacturing – turning designs into working tools that drive production.
Designing tools is both an art and a science – it requires technical skill and creative problem solving. With that qualification, you’ll be well on your way to a career in manufacturing and design that will be relevant to the future.
2. CNC machinist and programmer – The Digital Sculptor
- Role: Multi-axis machine operation, CNC code development (G-code/M-code), high-tech manufacturing precision.
- Skills: CNC operations, CAD/CAM programming and machining accuracy.
- Why It Matters: As the world transforms to industry 4.0 CNC programmers have become the front runners of smart manufacturing.
3. Tool Designer (CAD/CAM Specialist) – The Architect of Production
- Role: Design moulds, dies, jigs, and fixtures in CAD/CAM software such as CATIA, Creo or SolidWorks.
- Critical Competencies: 3D design, simulation and cost-effective tool development.
- Why It Matters: The inventors of the tools create the road map of production in such a way that mass production can be achieved without any complications.
4. Quality Control Engineer – The Perfectionist Behind Every Product
- Role: Inspect manufactured parts with the assistance of scanners, gauges, and CMMs to achieve zero defects.
- Key Skills: Metrology, compliance, precision testing.
- Why It Matters: QC professionals are in charge of product integrity, safety, and brand reputation.
5. Mould Designer & Maker – The Plastics Specialist
Role: Develop and design injection moulds into plastic components. It is utilized in all areas of modern life.
Major Skills: CNC machining, EDM processes, Injection moulding.
Why It Matters: As plastics are taking over industries around the world, the demands and supply of mould specialists are high and few.
Salary Outlook in India
- Freshers (0-1 years): ₹2.5 – ₹4.5 LPA (Also, it can go higher with expertise in CNC/CAD-CAM).
- Mid-Level (3–5 years): ₹5 – ₹8 LPA.
- Senior/Specialist Roles: ₹10 – ₹14+ LPA, exclusively in CNC programming and mould design.
All these are generic expectations according to industry trends. Higher levels of CAD/CAM, CNC technology, and precision design have a great impact on further earning potential.
Growth & Career Security in the Future
The tool designers cannot be substituted by AI and automation – they simply add value to the human expertise.
Tool design is a career that is future-safe and provides growth and stability.
Its opportunities cut across automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, healthcare, and defence.
Next Step: Post-Diploma in Tool design at NTTF
A Post Diploma in Tool Design by NTTF offers students excellent opportunities to accelerate in their careers through:
65% Practical Training – Industry Labs and Live Projects.
Sophisticated Skills CAD/CAM, CNC, mould design, precision engineering.
Placement Support – Good corporate relationship and 100% placement support.
The Road Ahead for Tool Engineers in Manufacturing
The diploma in Tool Engineering is not the goal – it will be the starting point of the life-long career in the field of innovation and manufacturing. The choice to be a:
- Master craftsperson (Tool and Die Maker),
- Digital sculptor (CNC Programmer),
- Production architect (Tool Designer),
- Quality guy (QC Engineer), or
- Plastics designer (Mould Designer),
Your experience will never be replaced in making industries the future.
Your career is waiting. Build it with confidence.