The Role of Electrical and Electronics Engineers in IOT Technology
March 22, 2024 2024-10-13 5:30The Role of Electrical and Electronics Engineers in IOT Technology

The Internet of Things (IoT) is a revolutionary concept that connects everyday objects and devices to the internet, enabling them to communicate, collect, and exchange data. Imagine a world where your refrigerator notifies you when you’re running low on groceries, or streetlights adjust their brightness based on traffic patterns – that’s the power of IoT. In essence, IoT transforms ordinary objects into smart, interconnected devices, creating a network of endless possibilities.
Importance of IoT in Various Industries:
- Healthcare: IoT enables remote patient monitoring, personalized treatment plans, and efficient healthcare delivery, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. This is particularly beneficial for professionals who have completed a diploma in electrical engineering or a diploma in EE, as they can leverage their expertise to design and implement IoT solutions tailored to the healthcare sector.
- Agriculture: IoT-powered sensors monitor soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and crop health, optimizing farming practices and enhancing crop yields. Professionals with an electrical diploma or a diploma in electrical engineering can utilize their skills to develop and deploy IoT systems that revolutionize agricultural processes, ensuring sustainable food production and agricultural efficiency.
- Manufacturing: IoT facilitates predictive maintenance, real-time inventory tracking, and supply chain optimization, leading to increased productivity and cost savings in manufacturing processes. Individuals with a diploma in electrical engineering or a related field play a crucial role in implementing IoT solutions within manufacturing facilities, leveraging their expertise to enhance efficiency and streamline operations.
- Smart Cities: IoT technologies drive urban development initiatives, including smart transportation systems, waste management solutions, and energy-efficient infrastructure, enhancing quality of life for citizens while promoting sustainability. Professionals with a diploma in electrical engineering or a diploma in EE are well-equipped to design and deploy IoT systems that contribute to the development of smart cities, leveraging their knowledge to create innovative solutions for urban challenges.
- Retail: IoT-enabled smart shelves, inventory tracking systems, and personalized shopping experiences revolutionize the retail industry, streamlining operations and enhancing customer engagement. Individuals with a background in electrical engineering or a diploma in electrical engineering can leverage their skills to develop and implement IoT solutions that transform the retail landscape, driving efficiency and improving the overall shopping experience for consumers.
Role of Electrical Engineers in IoT:
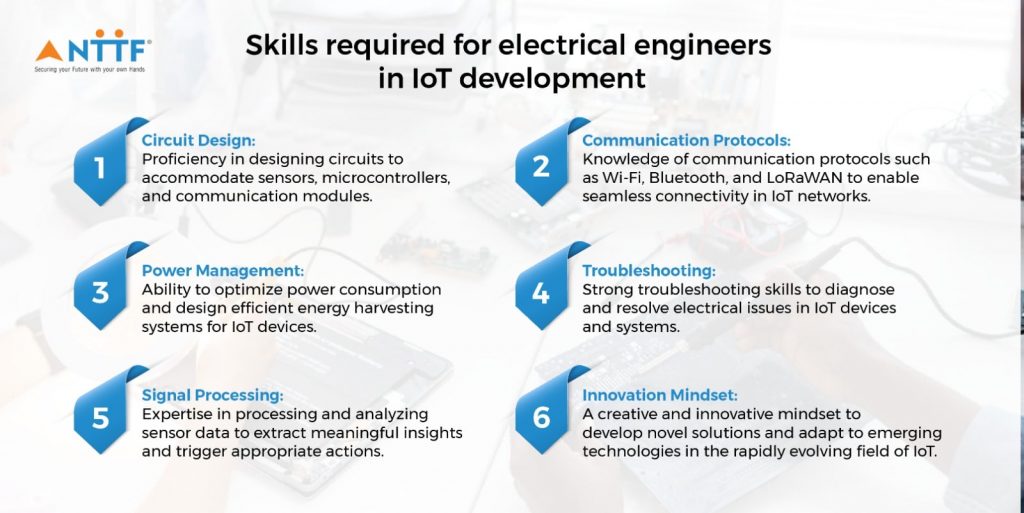
Electrical engineers play a crucial role in the development and implementation of IoT solutions. They are responsible for designing and optimizing the electrical systems that power IoT devices, ensuring efficient energy consumption and reliable operation. Additionally, electrical engineers are involved in the integration of sensors, actuators, and communication modules, enabling seamless connectivity and data exchange in IoT ecosystems. Their expertise in circuit design, power management, and signal processing is instrumental in creating robust and scalable IoT infrastructures that drive innovation across various industries.
Case study of a successful IoT project led by electrical engineers:
In a groundbreaking initiative, a team of electrical engineers led the development of an IoT-enabled smart grid system aimed at revolutionizing energy distribution and management. Leveraging their expertise in circuit design, power systems, and communication protocols, the team designed a network of smart meters equipped with sensors to monitor energy consumption in real-time. These smart meters were integrated with a centralized control system, allowing utility providers to remotely monitor and manage energy distribution, optimize load balancing, and detect potential faults or outages proactively.
Through seamless collaboration with software developers and data scientists, the team implemented advanced analytics algorithms to analyze the vast amounts of data collected from the smart meters. These insights were leveraged to optimize energy usage, reduce wastage, and enhance the overall efficiency of the grid. As a result of this innovative IoT solution, the utility provider witnessed significant improvements in grid reliability, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. This case study exemplifies the invaluable contributions of electrical engineers in driving transformative change through IoT technology.
Challenges and Future Trends
Implementing IoT solutions presents engineers with a myriad of challenges, ranging from technical hurdles to regulatory and security concerns. Some of the key challenges include:
- Interoperability: Integrating diverse IoT devices and platforms from different manufacturers while ensuring seamless communication and compatibility.
- Security: Safeguarding IoT devices and networks from cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Scalability: Designing IoT solutions that can scale to accommodate a growing number of devices and users without compromising performance or reliability.
- Data Privacy: Addressing concerns related to the collection, storage, and use of personal data generated by IoT devices, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- Power Consumption: Optimizing energy usage and implementing efficient power management strategies to prolong the battery life of IoT devices, especially in remote or inaccessible locations.
- Legacy Systems Integration: Integrating IoT solutions with existing legacy systems and infrastructure, overcoming compatibility issues and ensuring smooth transition and coexistence.
The emerging trends in IoT technology:
- Edge Computing: The shift towards processing data at the edge of the network, closer to where it is generated, to reduce latency, enhance security, and optimize bandwidth usage.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integration of AI and ML algorithms into IoT systems to analyze vast amounts of data, extract actionable insights, and enable autonomous decision-making.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks unlocking new opportunities for ultra-fast, low-latency communication, enabling real-time IoT applications in areas such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and immersive experiences.
- Blockchain Technology: Leveraging blockchain for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions and data exchanges in IoT networks, enhancing trust, integrity, and accountability.
- Sustainable IoT: Embracing sustainable practices and technologies to reduce the environmental footprint of IoT devices and systems, promoting energy efficiency, resource conservation, and circular economy principles.
The integral role of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (EE) in the IoT realm cannot be overstated. From designing circuits to optimizing power consumption, their expertise forms the backbone of interconnected smart systems that redefine industries. As we confront challenges such as interoperability and security, the future of IoT is bright, driven by innovations like edge computing, AI, 5G, blockchain, and sustainability. The journey of EE professionals, armed with their diploma in Electrical Electronics Engineering, continues to push boundaries, shaping a future where IoT transcends technology, becoming a force for global transformation.
NTTF, with multiple campuses in India, stands at the forefront of engineering education, equipping students with a robust foundation and practical skills with NCVET-recognized diplomas to thrive in the industry. With a curriculum emphasizing 60% practical training, NTTF trainees not only gain theoretical knowledge but also engage in hands-on experiences where they build machines and tools aligned with industry trends. This hands-on approach ensures that NTTF graduates are well-prepared to meet the demands of the ever-evolving IoT landscape, making meaningful contributions to innovation and technological advancement.